Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, L.*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Tomota, Yo*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinement
neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinementMao, W.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Morooka, Satoshi; Gao, S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 176, p.69 - 82, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The yield stress of Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) metastable austenitic steel increased 3.5 times (158  551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35
551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35  m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5
m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5  m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87
m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87  0.82).
0.82).  neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the
neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the  111
111 //LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the
//LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the  111
111 //LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
//LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Xu, P. G.; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 23 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Liu, X. J.*; Xu, P. G.; Shiro, Ayumi*; Zhang, S. Y.*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Akita, Koichi*; Zolotoyabko, E.*; Liss, K.-D.*
Journal of Materials Science, 57(46), p.21446 - 21459, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; Wang, L.*; Tang, B.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Kato, Hidemi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 129, p.251 - 260, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:95.2(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yang, J.*; Ren, W.*; Zhao, X.*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Miao, P.*; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Zhang, Z.*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 99, p.55 - 60, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-entropy alloys are characteristic of extensive atomic occupational disorder on high-symmetric lattices, differing from traditional alloys. Here, we investigate magnetic and thermal transport properties of the prototype face-centered-cubic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi by combining physical properties measurements and neutron scattering. Direct-current (dc) and alternating-current (ac) magnetizations measurements indicate a mictomagnetic behavior with coexisting antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic interactions in the entire temperature region and three anomalies are found at about 80, 50, and 20 K, which are related to the paramagnetic to antiferromagnetic transition, the antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic transition, and the spin freezing, respectively. The electrical and thermal conductivities are significantly reduced compared to Ni and the temperature dependence of lattice thermal conductivity exhibits a glass-like plateau. Inelastic neutron scattering measurements suggest weak anharmonicity so that the thermal transport is expected to be dominated by the defect scattering.
Hayakawa, Sho*; Doihara, Kohei*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Aichi, Masaatsu*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*
Journal of Materials Science, 54(17), p.11509 - 11525, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:56.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hayakawa, Sho*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Kawabata, Tomoya*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*
Journal of Materials Science, 54(16), p.11096 - 11110, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:42.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr MnO
MnO
Tokuda, Makoto*; Mashimo, Tsutomu*; Khandaker, J. I.*; Ogata, Yudai; Mine, Yoji*; Hayami, Shinya*; Yoshiasa, Akira*
Journal of Materials Science, 51(17), p.7899 - 7906, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) , C-SiO
, C-SiO , and C-SiC-SiO
, and C-SiC-SiO nanotubes
nanotubesTaguchi, Tomitsugu; Shamoto, Shinichi
Journal of Materials Science, 47(10), p.4363 - 4369, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:11.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Three types of composite nanotube heterostructures (two double-layered and one triple-layered structure) are synthesized by simple heat treatment, forming SiC-SiO , C-SiO
, C-SiO , and C-SiC-SiO
, and C-SiC-SiO composite coaxial nanotubes. These multilayered composite nanotubes consist of several components with different electrical properties, for example, metal, semiconductor and insulator components. In particular, C-SiC-SiO
composite coaxial nanotubes. These multilayered composite nanotubes consist of several components with different electrical properties, for example, metal, semiconductor and insulator components. In particular, C-SiC-SiO triple-layered nanotubes with metallic, semiconducting and insulating layers are synthesized for the first time. These multilayered nanotubes can be expected to find applications in nanoscale heterostructure electronic and optical devices.
triple-layered nanotubes with metallic, semiconducting and insulating layers are synthesized for the first time. These multilayered nanotubes can be expected to find applications in nanoscale heterostructure electronic and optical devices.
Kita, Kenichiro; Narisawa, Masaki*; Nakahira, Atsushi*; Mabuchi, Hiroshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Journal of Materials Science, 45(13), p.3397 - 3404, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:34.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized ceramic fibers based on silicon carbide (SiC) from polymer blends of polycarbosilane (PCS) and polymethylphenylsiloxane (PMPhS). PMPhS was compatible with PCS up to 30 mass%. The polymer blend was formed a transparent melt at temperatures higher than 513 K and the softening point was also lowered by adding PMPhS. 15 mass% of PMPhS to PCS was the most suitable condition for obtaining thin fibers with an average diameter of 14.4  m and the ceramic yield of the cured fiber was 85.5% after pyrolysis at 1273 K. In spite of the small diameter, the resulting tensile strength at 1273 K was rather limited at 0.78 GPa. After high temperature pyrolysis at 1673
m and the ceramic yield of the cured fiber was 85.5% after pyrolysis at 1273 K. In spite of the small diameter, the resulting tensile strength at 1273 K was rather limited at 0.78 GPa. After high temperature pyrolysis at 1673 1773 K, a porous nanocrystalline SiC fiber with a unique microstructure was obtained with surface area of 70
1773 K, a porous nanocrystalline SiC fiber with a unique microstructure was obtained with surface area of 70 150 m
150 m /g.
/g.
Kita, Kenichiro; Narisawa, Masaki*; Nakahira, Atsushi*; Mabuchi, Hiroshi*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Journal of Materials Science, 45(1), p.139 - 145, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:37.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The polymer blends of polycarbosilane (PCS) and polymethylohydrosiloxane with high molecular weight (PMHS-h) were prepared by freeze-drying process. Melt viscosity, themogravimetric analysis, and gas evolution from the polymer blends were analyzed. The polymer blend of HSah15 (15 mass% PMHS-h to PCS) was melt-spun to fiber form, curing by thermal oxidation and pyrolyzed at various temperatures up to 1773 K. The fibers were investigated by tensile tests, FE-SEM observation, and XRD (X-ray diffraction) analysis. After pyrolysis at 1273 K, there were amounts of pores in the cross sections of the fiber derived from HSah15, and after pyrolysis at 1773 K, no remarkable  -SiC crystal were formed on the outside surface of the fiber derived from HSah15.
-SiC crystal were formed on the outside surface of the fiber derived from HSah15.
 C
CChen, J.; Zhai, M.*; Asano, Masaharu; Huang, L.*; Maekawa, Yasunari
Journal of Materials Science, 44(14), p.3674 - 3681, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:59.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A poly(styrenesulfonic acid)-grafted polyetheretherketone (ssPEEK) polymer electrolyte membrane was developed by radiation grafting of ethyl styrenesulfonate (ETSS) onto PEEK film and subsequent hydrolysis. The long-term durability of the ssPEEK membrane was tested in a fuel cell, and it exhibited a lifetime of more than 1,000 h and a slow voltage degradation. After durability test, the catalyst layers were analyzed by XRD and TEM; the membrane was investigated by determining the change in thickness, proton conductivity and amounts of sulfonic acid groups. It was concluded that the degradation of performance in fuel cell was due to the thermal aging of the hydrocarbon membrane exposed to the electrochemical environment using the pure oxygen as the oxidant gas, as well as the Nafion-based catalyst layer being subject to high temperature for a long time, where the Pt catalyst was aggregated and sintered.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationFurusawa, Kazuya*; Kita, Erika*; Saeki, Toshihiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Nishi, Norio*; Dobashi, Toshiaki*
Journal of Biomaterials Science; Polymer Edition, 19(9), p.1159 - 1170, 2008/09
To insolubilize DNA for preparing a novel carcinogen adsorbent, effects of  -ray irradiation on aqueous solutions of mixtures of DNA with cross-linking biopolymers (CBP): gelatin, bovine serum albumin, carboxymethyl cellulose and hydroxyethyl-cellulose, O-[2-hydroxy-3-(trimethyl ammonio)-propyl], chloride have been studied. DNA-CBP hybrid gels were successfully prepared from aqueous mixtures of DNA with CBP in a limited range of irradiation dose. Gel fraction (Gf) and swelling ratio (S) of the hybrid gels were measured. The Gf and S of hybrid gels increased and decreased, respectively, with increasing irradiated dose. Adsorption of one of carcinogen, acridine orange, was also examined for the gels. From the experimental results, the optimum condition for preparing insolubilized homogeneous DNA gels was determined.
-ray irradiation on aqueous solutions of mixtures of DNA with cross-linking biopolymers (CBP): gelatin, bovine serum albumin, carboxymethyl cellulose and hydroxyethyl-cellulose, O-[2-hydroxy-3-(trimethyl ammonio)-propyl], chloride have been studied. DNA-CBP hybrid gels were successfully prepared from aqueous mixtures of DNA with CBP in a limited range of irradiation dose. Gel fraction (Gf) and swelling ratio (S) of the hybrid gels were measured. The Gf and S of hybrid gels increased and decreased, respectively, with increasing irradiated dose. Adsorption of one of carcinogen, acridine orange, was also examined for the gels. From the experimental results, the optimum condition for preparing insolubilized homogeneous DNA gels was determined.
Septiani, U.*; Chen, J.; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru; Kubota, Hitoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 42(4), p.1330 - 1335, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:47.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The influence of pre-irradiation atmosphere, argon and air, on radiation grafting of styrene into poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) films and the properties of the ETFE-based radiation-grafted polymer electrolyte membranes were investigated. The preparation and properties of the membranes were found to be strongly influenced by the  -ray pre-irradiation atmosphere. The proton conductivity was measured in its water-saturated state at 25
-ray pre-irradiation atmosphere. The proton conductivity was measured in its water-saturated state at 25 C, and the membrane durability was tested in a 3 % H
C, and the membrane durability was tested in a 3 % H O
O aqueous solution at 60
aqueous solution at 60 C. The proton conductivity of the membrane prepared by pre-irradiation under air was higher than that of the membrane prepared under argon with the same ion exchange capacity level. However, the durability of the former was considerably lower than that of the latter. For instance, the membrane with an ion exchange capacity of about 1.0 mmolg-1 prepared under argon was twice as durable as that prepared under air. It was considered that the lower durability of the membrane prepared by pre-irradiation under air was because of the unstable ether bond introduced between the graft chains and the backbone chains. : polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM); radiation grafting; styrene; durability; ETFE
C. The proton conductivity of the membrane prepared by pre-irradiation under air was higher than that of the membrane prepared under argon with the same ion exchange capacity level. However, the durability of the former was considerably lower than that of the latter. For instance, the membrane with an ion exchange capacity of about 1.0 mmolg-1 prepared under argon was twice as durable as that prepared under air. It was considered that the lower durability of the membrane prepared by pre-irradiation under air was because of the unstable ether bond introduced between the graft chains and the backbone chains. : polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM); radiation grafting; styrene; durability; ETFE
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tanaka, Shigeru; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ito, Masayoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 42(1), p.130 - 135, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have synthesized minute SiC products from polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid organosilicon polymer, with radiation curing. Since there is a close relationship between the properties of obtained SiC products and pyrolysis condition, it is important to investigate the ceramization process of PVS in order to find out the optimum pyrolysis condition. In this paper, the ceramization process of the PVS cured by  -ray irradiation at room temperature was investigated by gas analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, density measurement, and so on. It was found that the ceramization of
-ray irradiation at room temperature was investigated by gas analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, density measurement, and so on. It was found that the ceramization of  -ray cured PVS starts above 500K, and that drastic organic-inorganic conversion occurs in the temperature range of 700-1100K. According to the results of the changes of mass and density, it was found that the volume shrinkage of PVS during the curing and pyrolysis processes is 80%. The SiC obtained by pyrolysis at 1573K showed the density of 2.50g/cm
-ray cured PVS starts above 500K, and that drastic organic-inorganic conversion occurs in the temperature range of 700-1100K. According to the results of the changes of mass and density, it was found that the volume shrinkage of PVS during the curing and pyrolysis processes is 80%. The SiC obtained by pyrolysis at 1573K showed the density of 2.50g/cm and microvickers hardness of 31.6GPa.
and microvickers hardness of 31.6GPa.
Chen, J.; Asano, Masaharu; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yoshida, Masaru
Journal of Materials Science, 41(4), p.1289 - 1292, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:58.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The MeSt/tBuSt/DVB-grafted polymer electrolyte membrane showed a high performance for the fuel cell applications. The tBuSt contributed the high chemical stability while the MeSt contributed the high conductivity to the resulted membrane. The DVB crosslinker in the membrane further improved the chemical stability. The new polymer electrolyte membrane with a degree of grafting of 36% showed proton conductivity as high as the Gore-Select membrane, and the durability time was about 3 times longer than that of the traditional styrene/DVB-grafted one. Therefore, the MeSt/tBuSt/DVB-grafted polymer electrolyte membrane was more possible to be used for the fuel cells.
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ito, Masayoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 39(18), p.5689 - 5694, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation effect of  -ray on polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid organosilicon polymer, was investigated and the optimum curing condition to synthesize a minute SiC product with radiation curing was discussed. Room temperature and liquid nitrogen temperature (77K) were examined as the irradiation temperature. In both cases, the cured PVS maintaining its formed shape could be obtained by
-ray on polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid organosilicon polymer, was investigated and the optimum curing condition to synthesize a minute SiC product with radiation curing was discussed. Room temperature and liquid nitrogen temperature (77K) were examined as the irradiation temperature. In both cases, the cured PVS maintaining its formed shape could be obtained by  -ray irradiation under vacuum, and the cured PVS in solid state at room temperature was obtained by irradiation with dose of above 3-4MGy. It was found that the efficiency of crosslinking in case of the irradiation at room temperature is higher than that in case of irradiation at 77K. The PVS injected into a mold was irradiated by
-ray irradiation under vacuum, and the cured PVS in solid state at room temperature was obtained by irradiation with dose of above 3-4MGy. It was found that the efficiency of crosslinking in case of the irradiation at room temperature is higher than that in case of irradiation at 77K. The PVS injected into a mold was irradiated by  -ray with dose of 3.6MGy at room temperature under vacuum, and pyrolyzed at 1273 K in Ar gas atmosphere. As a result, minute SiC products which had similar shapes to the mold and the sizes of 30-60
-ray with dose of 3.6MGy at room temperature under vacuum, and pyrolyzed at 1273 K in Ar gas atmosphere. As a result, minute SiC products which had similar shapes to the mold and the sizes of 30-60 m were obtained.
m were obtained.
 and YVO
and YVO single crystal
single crystalSugiyama, Akira; Nara, Yasunaga; Wada, Kengo*; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu
Journal of Materials Science; Materials in Electronics, 15(9), p.607 - 612, 2004/09
Laser crystal bonding of a neodymium-doped yttrium orthovanadate (Nd: YVO ) and a non-doped yttrium orthovanadate (YVO
) and a non-doped yttrium orthovanadate (YVO ) crystal as a cold finger has been demonstrated. Instead of a traditional chemical treatment, a newly developed dry etching process was applied to the preparation for contact of mechanically polished surfaces. In the subsequent heat treatment process, stable heating at 873 K was required to prevent precipitation at the bonded interface. The bonded interface of 3 mm
) crystal as a cold finger has been demonstrated. Instead of a traditional chemical treatment, a newly developed dry etching process was applied to the preparation for contact of mechanically polished surfaces. In the subsequent heat treatment process, stable heating at 873 K was required to prevent precipitation at the bonded interface. The bonded interface of 3 mm  3 mm was investigated by optical scattering and wavefront distortion measurements. The scattering density around the bonded interface was less than 4.6
3 mm was investigated by optical scattering and wavefront distortion measurements. The scattering density around the bonded interface was less than 4.6 10
10 /cm
/cm and the wavefront distortion caused by the bonded region was assumed to be around 0.04-wave at 633 nm. Additional magnified inspection showed that atoms in the bonded region were well arranged with the same regularity as the bulk crystal. The diffusion coefficient of Nd
and the wavefront distortion caused by the bonded region was assumed to be around 0.04-wave at 633 nm. Additional magnified inspection showed that atoms in the bonded region were well arranged with the same regularity as the bulk crystal. The diffusion coefficient of Nd ions in the YVO
ions in the YVO crystal was estimated at 2.3
crystal was estimated at 2.3 10
10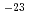 m
m /sec at 873 K.
/sec at 873 K.
Davies, A. R.*; Field, J. E.*; Takahashi, Koji; Hada, Kazuhiko
Journal of Materials Science, 39(5), p.1571 - 1574, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:33.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A four-point bend test was used to determine the fracture toughness of mechanical grade and di-electric (optical) grade chemical vapour deposited (CVD) diamond. The validity of the test was first confirmed by measuring the toughness of alumina and confirming the results with literature values. The toughnesses of both types of CVD were similar; 8.5 1.0 and 8.3
1.0 and 8.3 0.4 MPa (
0.4 MPa (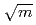 ) respectively. This is higher than the value of 3.4
) respectively. This is higher than the value of 3.4 0.5 MPa (
0.5 MPa (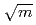 ) measured for diamond by Field and Freeman, 1981 using an indentation technique. It is suggested that this is primarily due to differences in surface roughness. There were enough samples to make a preliminary study of the effect of temperature and these data are reported.
) measured for diamond by Field and Freeman, 1981 using an indentation technique. It is suggested that this is primarily due to differences in surface roughness. There were enough samples to make a preliminary study of the effect of temperature and these data are reported.